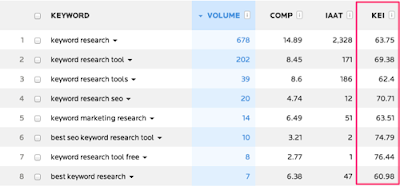
KEI (keyword
effectiveness index) is one of the quickest ways to find keywords that show
potential - that is, those keywords which are likely to help your site attract
more traffic. It looks a bit like this:
It's a scaled metric,
so you'll never see a KEI of more than 100.
KEI is a relative
factor that compares targeted keyword phrases to the number of pages competing
for these phrases. The results are stack-ranked based upon the chances for
success. The higher the KEI factor, the easier (theoretically) it should be to
obtain higher rank positions and targeted traffic for the given phrase. The
ideal is to find keyword phrases that are searched for often, but have
relatively little competition from other web sites.
KEI compares the search
popularity, or number of times that users search using a specific phrase, to
the number of web pages competing for that phrase. The results are always
relative to one another, so you can use any two sources that you wish. The
formula for calculating KEI is simply to square the search popularity for a
phrase and divide it by the number of competing pages.
In
algebraic form the formula looks like this:
KEI = No. of Results / No. of Searches
Example
Let's us there are
around 130000 competing webpage’s for a particular keyword having around 380
searches a month then KEI would be calculated as follows:-
KEI = 130000/380 = 342.10
The lower the KEI, the better your chances of ranking.
The greater the KEI, the lesser your chances of ranking.
It is important that
your target group is able to find you in the search engines. Your website will
only show up in the search engine result page when your website has got content
on it which matches the search queries of your potential clients. But there are
a lot more aspects which determine your page rank in the search results.
“Targeting
keywords with a high KEI will help you rank better in the search engines.”
You will have to use
these keywords in the content of your website and we will use these keywords
for the title tags, headers, alt tags, meta tags, inbound and outbound links.